Highlights
- 100% interest in a large land package directly east of the Kinross Great Bear Dixie Project.
- Covers nearly 10 kilometres of east-trending interpreted structural trends known to host the Great Bear Dixie gold deposit.
- No drilling in the Dixie East area for more than 30 years; historical work focused on base metals at the eastern margin.
- Geological similarities to the Great Bear deposit including felsic tuffs, sericite schists, quartz feldspar porphyry, shearing, quartz veins, and sulphide mineralization.
- Historical work reported zinc and copper values on and proximal to the Dixie East property.
- Kinross presentations show the LP Fault structure extending eastward from the Dixie deposit across the Dixie East property.
Overview
The Dixie East Project is located 5.5 kilometres east of Kinross’ world-class Great Bear Dixie deposit, southeast of Red Lake, Ontario. BTU Metals has acquired a 100% interest in this significant new land package, which positions the Company directly along the eastern extension of structural trends that host the Great Bear discovery. The project remains virtually unexplored for LP Fault style gold mineralization and provides BTU with a compelling new exploration opportunity in one of Canada’s most active gold districts.
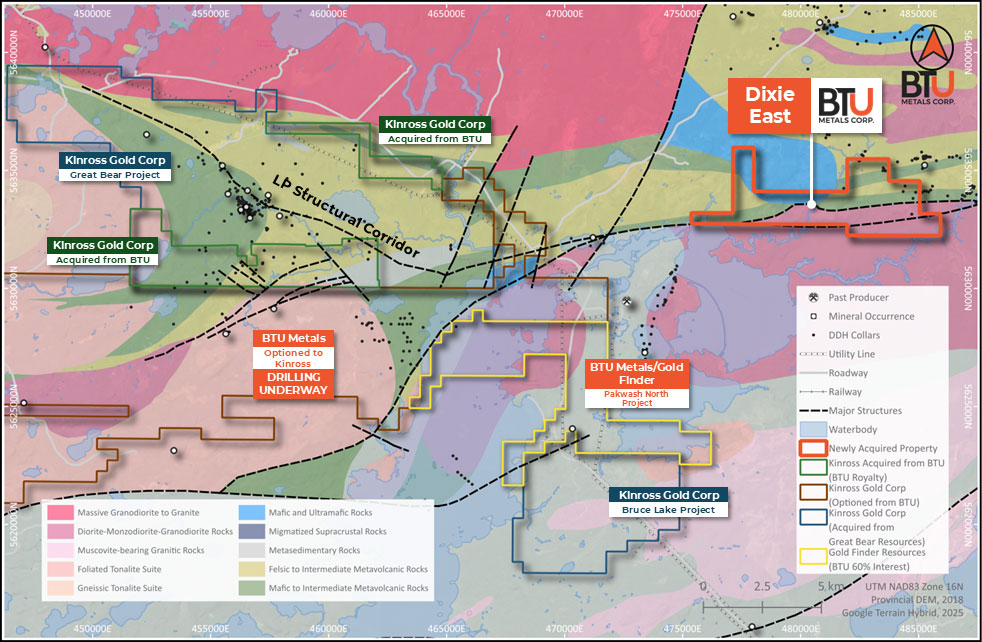
Historic Work
No drilling has been completed on the Dixie East ground in over 30 years, and earlier programs in the 1990s targeted base metals rather than gold. Limited historical work identified favourable lithologies and deformation, but the project remains essentially untested.
Geology
The Dixie East Project is underlain by geological units similar to those that host Kinross’ Great Bear Dixie mineralization. Historical drilling and mapping identified felsic volcanic tuffs, sericite schists, and quartz feldspar porphyry intrusions. These units are structurally deformed, with shearing, quartz veining, and associated sulphide mineralization. Past exploration recorded zinc and copper mineralization in and around the property. Importantly, Kinross has publicly illustrated the LP Fault structure extending eastward to the Dixie East property, aligning with the same regional system that controls mineralization at Great Bear.